Greater Trochanteric Bursitis
By Meghan Walter, SPT
What are bursae?
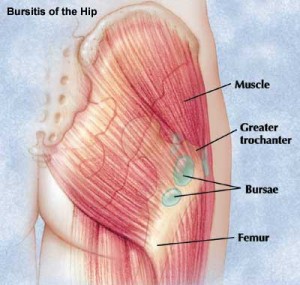
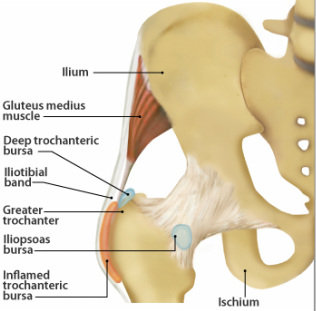
Bursae are fluid filled sacs that provide cushioning between bones and surrounding soft tissues. There are three to four bursae surrounding a large bony prominence on the femur (thigh bone), the greater trochanter (outside hip bump). These busae provide cushioning for the gluteus medius tendon, the iliotibial band (IT band), and the tensor fascia latae muscle.
How do they get irritated?
These bursae can get irritated and inflamed for a variety of reasons:
- Frictional trauma from muscle over-use. You can over-work your hip muscles by doing repetitive activities such as running, jumping, stair climbing, and squatting without giving them time to rest.
- Direct trauma to the side of the hip. This can come about from falling on the hip or getting hit on your side during a high impact sport like football or hockey.
- IT band tightness. Since your IT band lays right on top of the bursae, it puts excessive pressure on it causing frictional trauma when it tightens.
Greater trochanteric bursitis can also be a symptom of an underlying condition. It is commonly associated with gluteus medius dysfunction, lumbar spine disorders, leg-length discrepancy, and obesity. With these conditions, the biomechanics of the legs are altered causing abnormal force vectors through the hip, predisposing the bursae to irritation via frictional trauma.
How does it feel?
The outside of the upper hip is usually very tender to the touch. At first the pain is sharp, but gradually becomes a dull, aching pain that can radiate to the buttock and down the outside leg. Pain is usually accompanied by stiffness in the hip joint. The pain intensifies when lying on the side and while doing normal activities such as walking, running, sitting, and standing for prolonged periods of time.
How can we help?
Injections and surgical removal of the bursae are not the only option! There are several conservative and effective ways that physical therapists can get you back to doing the activities you love, pain-free!
- Pain relief. Your PT can implement a combination of techniques like ice massage and ultrasound to help reduce the pain and inflammation in the bursae.
- Range of motion. Depending on the cause of the inflammation, you may have limited motion in your back, hip, or knee. Your PT will teach you specific stretches to improve your flexibility and reduce friction.
- Manual therapy. To further help treat your condition, your PT will provide a variety of specialized hands-on techniques to your muscles and joints that will decrease your pain and increase your motion.
- Strengthening. Your PT will assess where your specific muscle imbalances are and design a strengthening program that is tailored to your specific needs and goals. Your program may include strengthening these key muscle groups- gluts, abdominals, and quads.
- Functional training. Once you are in less pain, have greater flexibility, and your muscle imbalances are corrected, your PT will begin to incorporate functional strengthening exercises into your sessions to help integrate you back into your daily activities. Performing these functional exercises under the careful eye of your PT will help reduce the risk of re-irritating the bursae while doing your normal activities outside of PT.
- Patient Education. It is important for you to understand how your bursitis came about and how you can avoid it happening again. Your PT will discuss with you everything you need to know about your condition and help you identify other factors that are contributing to your pain, such as faulty footwear or repetitive exercise regimen. Your PT will provide guidance on changing these factors and even help you design an exercise program that meets your goals and allows you to return to all of your activities pain-free.