by Brittany Brooks, SPT
What Is T4 Syndrome?
T4 syndrome is a musculoskeletal related dysfunction in which neurological structures are affected. This is caused by thoracic vertebrae being hypomobile, causing impingement on nerve fibers. Hypomobility can be caused by hunched posture, immobility, arthritic related disease, and inherited by genetics. Commonly, the sympathetic nervous system is most affected due to its nerve fibers being located at the T4 vertebrae. The sympathetic nervous system is important in regulating the respiratory and cardiovascular system as well as localized responses (ex. sweating).
The Thoracic Region:
The thoracic region contains 12 vertebrae numbered T1-T12. Each thoracic vertebrae have facets located on the sides of each which articulate or connect with the ribs. This connection makes thoracic vertebrae much more stable than cervical or lumbar vertebrae which do not have articulations with other bony structures. Also associated with the thoracic vertebrae are the thoracic nerve roots which sit underneath each vertebrae and connect to the spinal cord. In T4 syndrome the T4 nerve root is being compressed by a hypomobile segment.
T4 Syndrome Symptoms & Signs
Paresthesias in the hands following a “glove” distribution
- Headache
- Upper limb and neck pain
- Loss of coordination in the hands
- Heaviness of the upper extremities
- Tenderness upon palpation of T4 vertebrae
- Hypomobility of thoracic spine
- Pain with deep breath, cough, or sneeze
Risk Factors:
- Poor or hunched posture
- Immobility of the thoracic spine
- Poor core strength
- Inactivity
- Muscle imbalances
- Inappropriate lifting mechanics
T4 Syndrome Physical Therapy Treatment:
- Postural Correction: Clinicians are able to identify possible posture deviations which may result in T4 compression. Education can be given in order to adjust postural mechanics and change ergonomics throughout a patient’s daily schedule.
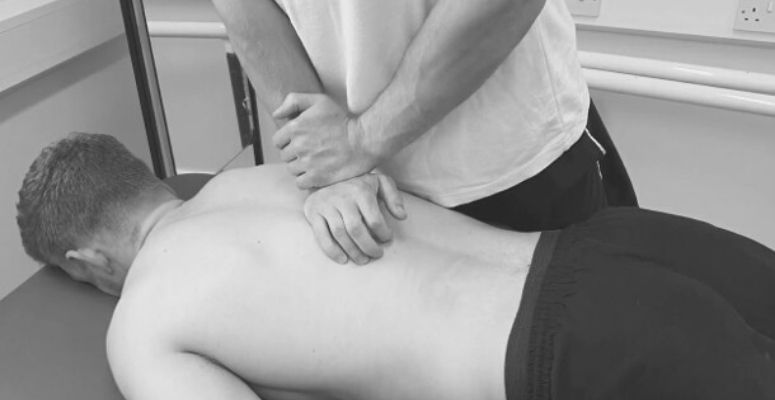
- Manual Therapy: Clinicians are trained in specific joint mobilizations in order to increase the mobility of thoracic segments. Also, manual technique can be used on surrounding structures to decrease tissue tension and tightness.
- Range of Motion and Stretching: T4 syndrome may result in decreased range of motion of the thoracic spine as well as the upper limbs. Clinicians are able to assist in range of motion and stretch surrounding muscles that may contribute to nerve fiber compression.
- Strengthening: T4 syndrome may result in weakness of upper limb and hand muscles which should be a primary target of physical therapy. Clinicians are able to provide exercises which target specific muscle groups located in those areas.
For more information or to make an appointment at any of our Capital Region clinics located in Malta, Queensbury, or Saratoga by calling 518-289-5242. Our therapists will develop a personalized program specific to your diagnosis.